Content-Based Routing
home
You can look through and run this example application to learn the basics of using Anypoint Studio to route messages in a flow by using a Choice router.
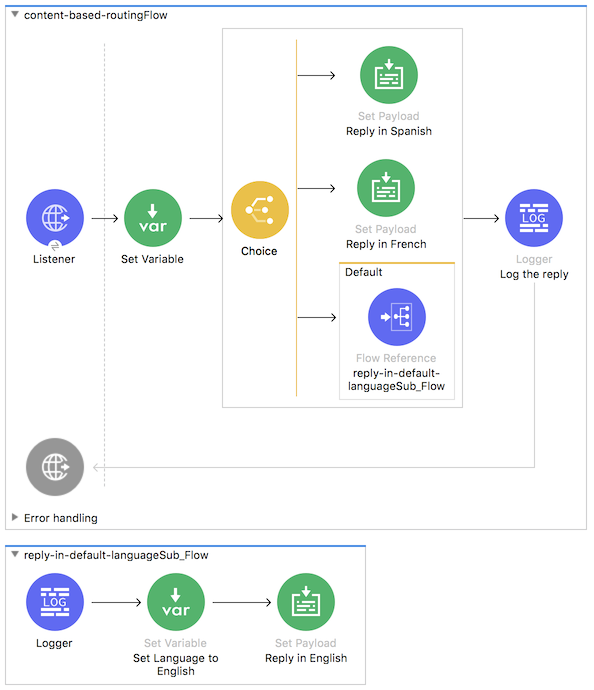
This example application performs the following actions:
- Listens for messages.
- Passes messages to a Set Variable component that sets the variable
languageto the language that is passed in the message by the parameterlanguage. Uses a Choice router to find out whether each message contains a
languageattribute. The presence and value of this attribute determine how the Choice router routes the message:- If the value is
French, the router routes the message to a Set Payload component that is named Reply in French. This latter component returns the messageBonjour!to the requester. - If the value is
Spanish, the router routes the message to a Set Payload component that is named Reply in Spanish. This latter component returns the messageHola!to the requester. If the message contains no
languageattribute, the router routes the message to the default path, which is a subflow that:- Logs the message "No language specified. Using English as a default." to the console
- Sets the value of
languagetoEnglish. - Returns the message
Hello!.
- If the value is
This example demonstrates that, when you are planning to route messages in a flow by using a Choice router, there are four aspects to planning that you need to consider:
- The content that the Choice router evaluates to determine how it routes messages
- The number of routes
- The default routing option
- The processing that the flow performs for each routing option
Set Up and Run the Example
- Open the Content-Based Routing project in Anypoint Studio. If you don't have Anypoint Studio installed, you can download it here.
- In the application in Studio, click the Global Elements tab.
- Double-click the HTTP Listener global element to open its Global Element Properties dialog.
- Change the contents of the Port field to 8081, if it is not set to that port already.
- Click each component in the message flow and view its properties.
- Click Configuration XML at the bottom of the editor and familiarize yourself with the XML of the application.
- Run the project by right-clicking its main folder and selecting Run As > Mule Application.
- Open any web browser, paste the following URL in the address bar, and press Enter: http://localhost:8081/?language=Spanish Result: Your browser presents a message that reads "Hola!".Check the console log in Studio and look for a log message that is similar to this one: INFO 2017-09-08 13:24:01,695 [[MuleRuntime].io.03] org.mule.runtime.core.api.processor.LoggerMessageProcessor: The reply "Hola!" means "hello" in Spanish.
- In your browser’s address bar, replace the current URL with this one, and then press Enter: http://localhost:8081/?language=French Result: Your browser presents a message that reads "Bonjour!". Check the console log in Studio again and look for a log message that is similar to this one: INFO 2017-09-08 13:26:01,695 [[MuleRuntime].io.03] org.mule.runtime.core.api.processor.LoggerMessageProcessor: The reply "Bonjour!" means "hello" in French.
- Try accessing
localhost:8081without specifying a language: http://localhost:8081 Result: Your browser presents a message that reads "Hello!".Check the console log in Studio again and look for a log message that are similar to these:
INFO 2017-09-08 13:27:01,691 [[MuleRuntime].io.03] org.mule.runtime.core.api.processor.LoggerMessageProcessor: No language specified. Using English as a default.
INFO 2017-09-08 13:27:01,695 [[MuleRuntime].io.03] org.mule.runtime.core.api.processor.LoggerMessageProcessor: The reply Hello! means "hello" in English