Database to Salesforce User Migration
home
Moves a large set of users from a database to Salesforce. You can trigger this manually or programmatically with an HTTP call. Users are upserted so that the migration can be run multiple times without worrying about creating duplicates.
This template uses batch to efficiently process many records at a time. A database table schema is included to make testing this template easier.
Note: In the following video, references to DataMapper have been replaced in the template with DataWeave transformations.
License Agreement
This template is subject to the conditions of the MuleSoft License Agreement.
Review the terms of the license before downloading and using this template. You can use this template for free with the Mule Enterprise Edition, CloudHub, or as a trial in Anypoint Studio.
Use Case
As a Salesforce administrator I want to synchronize Users from a database to Salesfoce.
This template helps you migrate users from a database to a Salesforce instance, specify filtering criteria, and set the behavior if an user already exists in the destination organization.
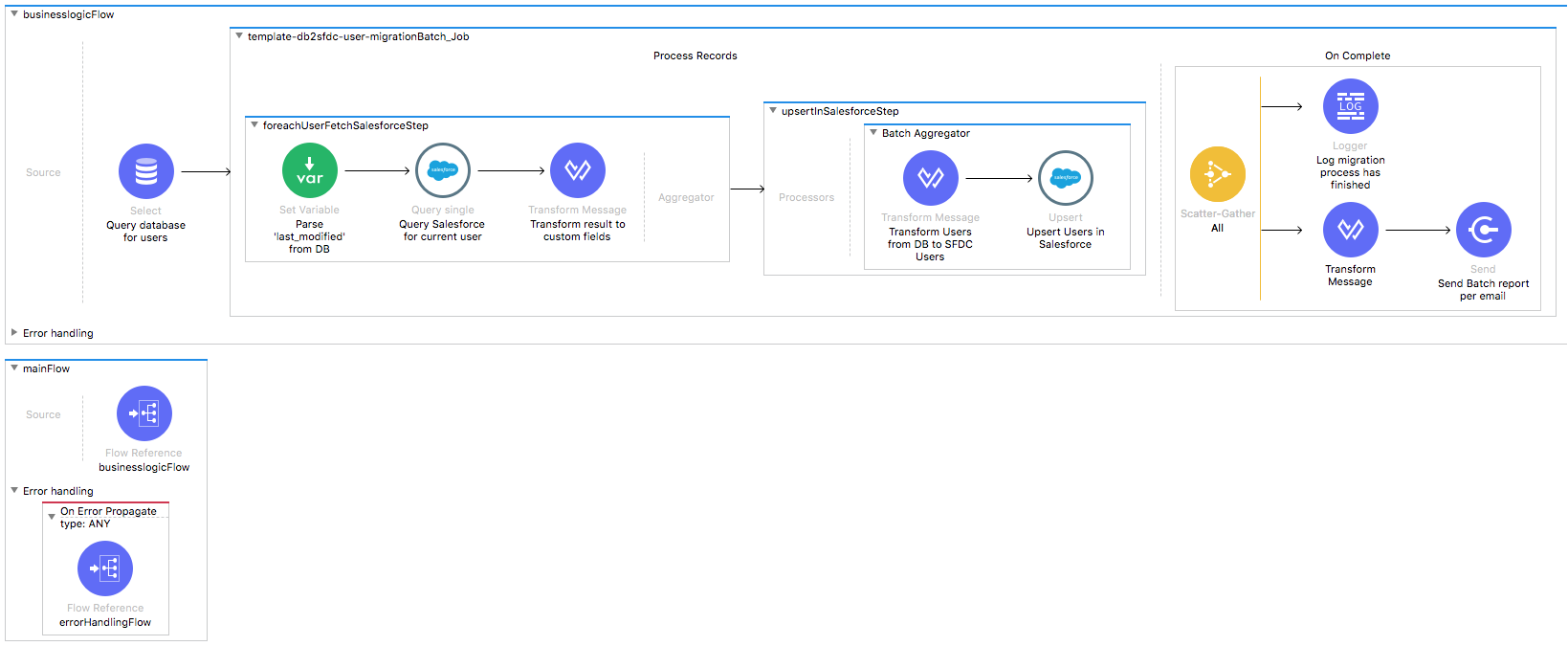
This template leverages the batch module.
The batch job is divided into Process Records and On Complete stages.
- First, the template browses to the database and queries all existing Users that match the filter criteria.
- During the Process stage, each database user is filtered depending on if it has an existing matching user in the Salesforce organization.
- The last step of the Process stage groups the users and upserts them into Salesforce.
- Finally during the On Complete stage, the template outputs statistics data to the console and sends notification email with the results of the batch execution.
Considerations
This template is customized for MySQL. To use it with a different SQL implementation, some changes are necessary.
After you import your template into Anypoint Studio, follow these steps to run it:
- Locate the properties file
mule.dev.properties, in src/main/resources. - Complete all the properties required as per the examples in "Properties to Configure".
- Add a dependency for your database dth eGlobal Elements section of the config flow to use your database-specific driver.
- By default this template relies on existing table user in the database of your choice, so it performs SQL statements against this table, but feel free to customize prepared statements to use a different database table or columns.
- Script for creating database table (MySQL syntax):
CREATE TABLE `sf_user` ( `firstname` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `lastname` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `salesforce_id` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `email` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) )
- Optionally customize query templates in
businessLogic.xmlif they don't match the SQL grammar of the database of your choice. - Once that is done, right click your template project folder.
- Click Run As > Mule Application.
Database Considerations
To get this template to work:
This template may use date time or timestamp fields from the database to do comparisons and take further actions.
While the template handles the time zone by sending all such fields in a neutral time zone, it cannot handle time offsets.
We define time offsets as the time difference that may surface between date time and timestamp fields from different systems due to a differences in the system's internal clock.
Take this in consideration and take the actions needed to avoid the time offset.
As a Data Source
There are no considerations with using a database as a data origin.
Salesforce Considerations
Here's what you need to know about Salesforce to get this template to work.
FAQ
- Where can I check that the field configuration for my Salesforce instance is the right one? See: Salesforce: Checking Field Accessibility for a Particular Field
- Can I modify the Field Access Settings? How? See: Salesforce: Modifying Field Access Settings
As a Data Destination
There are no considerations with using Salesforce as a data destination.
Run it!
Simple steps to get Database to Salesforce User Migration running.
Example of the output you see after browsing to the HTTP endpoint:
{
"Message": "Batch Process initiated",
"ID": "7fc674b0-e4b7-11e7-9627-100ba905a441",
"RecordCount": 32,
"StartExecutionOn": "2018-12-19T13:24:03Z"
}Running On Premises
In this section we help you run your template on your computer.
Where to Download Anypoint Studio and the Mule Runtime
If you are a newcomer to Mule, here is where to get the tools.
Importing a Template into Studio
In Studio, click the Exchange X icon in the upper left of the taskbar, log in with your
Anypoint Platform credentials, search for the template, and click Open.
Running on Studio
After you import your template into Anypoint Studio, follow these steps to run it:
- Locate the properties file
mule.dev.properties, in src/main/resources. - Complete all the properties required as per the examples in the "Properties to Configure" section.
- Right click the template project folder.
- Hover your mouse over
Run as - Click
Mule Application (configure) - Inside the dialog, select Environment and set the variable
mule.envto the valuedev - Click
Run
Running on Mule Standalone
Complete all properties in one of the property files, for example in mule.prod.properties and run your app with the corresponding environment variable. To follow the example, this is mule.env=prod.
After this, to trigger the use case, browse to the local HTTP endpoint with the port you configured in your file. For example for port 9090, browse to http://localhost:9090/migrateUsers, which creates a CSV report and sends it to the emails you set.
Running on CloudHub
While creating your application on CloudHub (or you can do it later as a next step), go to Runtime Manager > Manage Application > Properties to set the environment variables listed in "Properties to Configure" as well as the mule.env.
Once your app running, if you choose the sfdcusermigration domain name, to trigger the use case browse to http://sfdcusermigration.cloudhub.io/migrateusers, the program invokes, and a report is sent to the emails you configured.
Deploying your Anypoint Template on CloudHub
Studio provides an easy way to deploy your template directly to CloudHub, for the specific steps to do so check this
Properties to Configure
To use this template, configure properties (credentials, configurations, etc.) in the properties file or in CloudHub from Runtime Manager > Manage Application > Properties. The sections that follow list example values.
Application Configuration
- http.port
9090
Salesforce Connector Configuration for Company A
- sfdc.a.username
bob.dylan@example.com - sfdc.a.password
DylanPassword123 - sfdc.a.securityToken
avsfwCUl7apQs56Xq2AKi3X - user.localeSidKey
en_US - user.languageLocaleKey
en_US - user.timeZoneSidKey
America/New_York - user.emailEncodingKey
ISO-8859-1
Database Connection URL
- db.host
localhost - db.port
3306 - db.user
user-name - db.password
user-password - db.databasename
dbname
SMTP Services Configuration
- smtp.host
smtp.example.com - smtp.port
587 - smtp.user
exampleuser - smtp.password
examplepassword
Email Details
- mail.from
batch.migrateUsers.migration%example.com - mail.to
polly.hedra@example.com - mail.subject
Batch Job Finished Report
API Calls
Salesforce imposes limits on the number of API calls that can be made. Therefore calculating this amount is important. The template calls to the API can be calculated using this formula:
X + 1 / 200
X is the number of users to synchronize on each run.
Divide by 200 because by default, users are gathered in groups of 200 for each upsert API call in the commit step.
For instance if 10 records are fetched from an origin instance, then 11 API calls are made (10 + 1).
Customize It!
This brief guide intends to give a high level idea of how this template is built and how you can change it according to your needs.
As Mule applications are based on XML files, this page describes the XML files used with this template.
More files are available such as test classes and Mule application files, but to keep it simple, we focus on these XML files:
- config.xml
- businessLogic.xml
- endpoints.xml
- errorHandling.xml
config.xml
Configuration for connectors and configuration properties are set in this file. Even change the configuration here, all parameters that can be modified are in properties file, which is the recommended place to make your changes. However if you want to do core changes to the logic, you need to modify this file.
In the Studio visual editor, the properties are on the Global Element tab.
businessLogic.xml
The functional aspect of this template is implemented in this XML, directed by a flow responsible for excecuting the logic.
For the purpose of this template, the mainFlow excecutes a batch job which handles all its logic.
This flow has an exception strategy that basically consists of invoking the defaultChoiseExceptionStrategy defined in errorHandling.xml file.
endpoints.xml
This is the file where you find the inbound and outbound sides of your integration app.
This template has only an HTTP Listener connector as the way to trigger the use case.
Inbound Flow
HTTP Listener Connector - Start Report Generation
${http.port}is set as a property to be defined either on a property file or in CloudHub environment variables.- The path configured by default is
migrateUsersand you are free to change for the one you prefer. - The host name for all endpoints in your CloudHub configuration is
localhost. CloudHub routes requests from your application domain URL to the endpoint. - The endpoint is a request-response and a result of calling it, fetches the response with the total records by the criteria specified.
errorHandling.xml
This is the right place to handle how your integration reacts depending on the different exceptions.
This file provides error handling that is referenced by the main flow in the business logic.