Marketo to Salesforce Lead Broadcast
home
This template synchronizes leads from a Marketo instance to multiple Salesforce instances located in different regions. The integration polls changes from Marketo and routes leads to an appropriate Salesforce instance based on the lead location. For example, leads from EMEA only route to a Salesforce instance located in EMEA.
This template uses the publish-subscribe pattern, so anytime a new lead or a change to an existing lead occurs, the integration publishes the changes to a JMS topic and each subscriber application updates records in the target system.
The template consists of two different batch processes that consume the JMS topic, and based on the location, routes the leads to either the Salesforce instance in North America or to EMEA. In addition, this template logs output data to the console to keep you informed of changes.
License Agreement
This template is subject to the conditions of the MuleSoft License Agreement. Review the terms of the license before downloading and using this template. You can use this template for free with the Mule Enterprise Edition, CloudHub, or as a trial in Anypoint Studio.
Use Case
As a Marketo admin I want to synchronize leads between Marketo and Salesforce organizations.
This template provides an online sync of leads from a Marketo instance to a Salesforce instance. Each time a new lead or a change in an existing lead occurs, this integration polls for changes in the Marketo source instance and updates the lead in the target organization.
Requirements have been set not only to be used as examples, but also to establish a starting point to adapt your integration to your requirements.
This template leverages the Mule batch module. The batch job is divided in Process and On Complete stages.
The integration is triggered by a scheduler defined in the endpoints.xml file. The application queries and receives newest Marketo updates and creates and adds them to one of the JMS topics depending on the country for the lead record.
The application has two different batch jobs consuming JMS topics, one for migrating the changes to the first Salesforce organization (leads located in 'US') and the other for migrating the changes to the other Salesforce organization (leads located outside the 'US').
During the Process stage, each Salesforce lead is matched with an existing lead in the target system by email.
The last step of the Process stage groups the leads and creates or updates them in the Salesforce organization.
Finally during the On Complete stage the template logs output statistics data to the console.
Considerations
To make this template run, there are certain preconditions that must be considered. All of them deal with the preparations in both source and destination systems, that must be made for the template to run smoothly. Failing to do so could lead to unexpected behavior of the template.
Salesforce Considerations
Here's what you need to know about Salesforce to get this template to work:
- Where can I check that the field configuration for my Salesforce instance is the right one? See: Salesforce: Checking Field Accessibility for a Particular Field.
- Can I modify the Field Access Settings? How? See: Salesforce: Modifying Field Access Settings.
As a Data Destination
There are no considerations with using Salesforce as a data destination.
Marketo Considerations
As a Data Source
There are no considerations with using Marketo as a data origin.
Run it!
Simple steps to get this template running.
Running On Premises
In this section we help you run this template on your computer.
Where to Download Anypoint Studio and the Mule Runtime
If you are new to Mule, download this software:
Note: Anypoint Studio requires JDK 8.
Importing a Template into Studio
In Studio, click the Exchange X icon in the upper left of the taskbar, log in with your Anypoint Platform credentials, search for the template, and click Open.
Running on Studio
After you import your template into Anypoint Studio, follow these steps to run it:
- Locate the properties file
mule.dev.properties, in src/main/resources. - Complete all the properties required as per the examples in the "Properties to Configure" section.
- Right click the template project folder.
- Hover your mouse over
Run as. - Click
Mule Application (configure). - Inside the dialog, select Environment and set the variable
mule.envto the valuedev. - Click
Run.
Running on Mule Standalone
Update the properties in one of the property files, for example in mule.prod.properties, and run your app with a corresponding environment variable. In this example, use mule.env=prod.
Running on CloudHub
When creating your application in CloudHub, go to Runtime Manager > Manage Application > Properties to set the environment variables listed in "Properties to Configure" as well as the mule.env value.
Deploying a Template in CloudHub
In Studio, right click your project name in Package Explorer and select Anypoint Platform > Deploy on CloudHub.
Properties to Configure
To use this template, configure properties such as credentials, configurations, etc.) in the properties file or in CloudHub from Runtime Manager > Manage Application > Properties. The sections that follow list example values.
Application Configuration
- scheduler.frequency
60000 - scheduler.start.delay
0 - watermark.default.expression
2018-05-13T03:00:59Z - page.size
200
Salesforce Connector configuration for company A
- sfdc.a.username
bob.dylan@orga - sfdc.a.password
DylanPassword123 - sfdc.a.securityToken
avsfwCUl7apQs56Xq2AKi3X
Salesforce Connector configuration for company B
- sfdc.b.username
joan.baez@orgb - sfdc.b.password
JoanBaez456 - sfdc.b.securityToken
ces56arl7apQs56XTddf34X
Marketo Connector Configuration
- mkto.clientId
clientReachPointId - mkto.clientSecret
clientReachPointSecret - mkto.basePath
/ - mkto.host
marketo.mktorest.com - mkto.accessTokenUrl
https://marketo.mktorest.com/identity/oauth/token
JMS Connector Configuration
- jms.username
admin - jms.password
admin - jms.brokerUrl
tcp://localhost:61616
API Calls
Salesforce imposes limits on the number of API calls that can be made. Therefore calculating this amount may be an important factor to consider.
This template calls to the API can be calculated using this formula:
1 + X + X / ${page.size} -- X is the number of leads to synchronize on each run.
Divide by ${page.size} because by default the leads are gathered in groups of ${page.size} for each Upsert API call in the aggregation step. Also consider that these calls are executed repeatedly every polling cycle.
For instance if 10 records are fetched from the origin instance, then 12 API calls are made (1 + 10 + 1).
Customize It!
This brief guide provides a high level understanding of how this template is built and how you can change it according to your needs. As Mule applications are based on XML files, this page describes the XML files used with this template. More files are available such as test classes and Mule application files, but to keep it simple, we focus on these XML files:
- config.xml
- businessLogic.xml
- endpoints.xml
- errorHandling.xml
config.xml
This file provides the configuration for connectors and configuration properties. Only change this file to make core changes to the connector processing logic. Otherwise, all parameters that can be modified should instead be in a properties file, which is the recommended place to make changes.
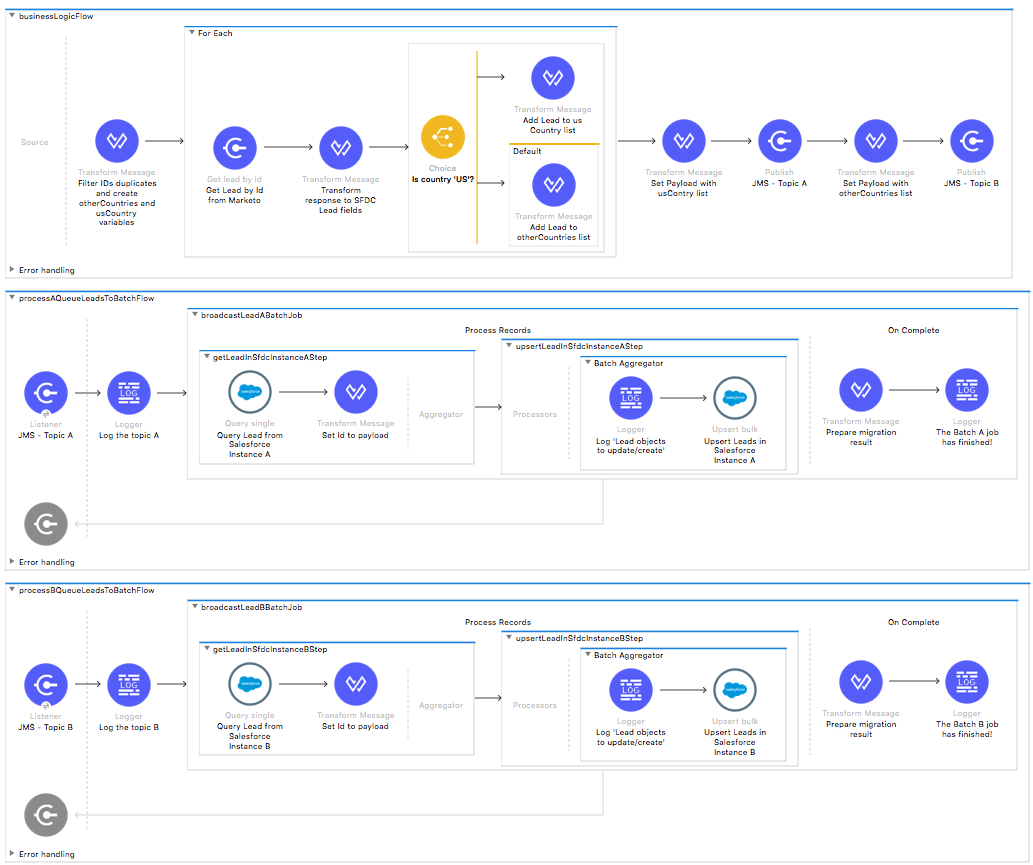
businessLogic.xml
Functional aspect of the template is implemented in this XML, directed by mainFlow, which deduplicates leads by ID, create two separate collections depending on the lead's country field and send them through two different topics for further processing.
Flows processAQueueLeadsToBatchFlow and processBQueueLeadsToBatchFlow get data from specific JMS topic and start executing specific batch.
There are two batches. Both have the same logic, but the first adds leads into Salesforce instance A and the other one adds leads to Salesforce instance B.
The batch logic is:
- During the Process stage, each Salesforce lead is matched with an existing lead in the target system by email.
- The Process stage groups the leads and creates or updates them in the Salesforce organization.
- During the On Complete stage, the batches logs output statistics data into the console.
endpoints.xml
This file contains a scheduler that periodically queries Marketo for updated or created fields - firstName,lastName,email,company,country of lead objects and then executes the mainFlow implemented in businessLogic.xml.
errorHandling.xml
This file handles how your integration reacts depending on the different exceptions. This file provides error handling that is referenced by the main flow in the business logic.