preregcain
Home | EN
Ad hoc API for CAINIAO to do the differents preregisters in Correos systems. This API transforms the request to the Correos standards and propagates the message to his internal processment, this is an asincronous behaviour so the API doesn't wait for a response from other application, the final API response only will inform if the message has been sent succesfully or not.
Because of this API has been designed exclusively for CAINIAO, the definition of the input and output interface has been adapted to its structure and type of data.
The actual operations for this API are:
- Boxes or pallets preregistes
- Orders preregisters
- Reverse logistic orders preregisters
- Customs update of orders preregisters
- Cancelation of preregistered orders
Policy rule
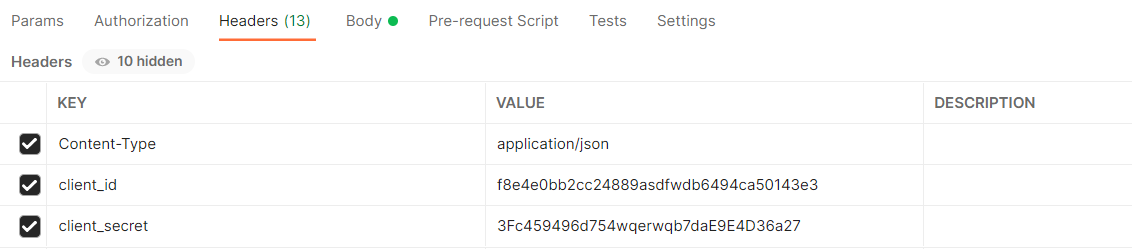
This API has the security policy named "Client ID Enforcement", https://docs.mulesoft.com/api-manager/2.x/client-id-based-policies. First, the client application has to request access to this API, then a pair of client_id and client_secret will be provided. Once the request is accepted by the API owners, the client will be granted to do requests to the API if the HTTP request headers "client_id" and "client_secret" are correctly set.
API REST use introduction
REST APIs use Uniform Resource Identifiers (URI) to address resources. Properly done URIs layouts would clearly communicate the API resource, such as:
http://example.restapi.es/france/paris/louvre/leonardo-da-vinci/mona-lisaAn incorrect design of URIs would give a much more difficult resource to understand like:
http://example.restapi.es/68dd0-a9d3-11e0-9f1c-0800200c9a66URI format
The generic URI syntax is defined as follows:
URI = scheme "://" authority "/" path [ "?" query ] [ "#" fragment ]
- scheme: The scheme identifies the protocol to access the resources, it can be HTTP (without SSL) or HTTPS (with SSL). It is made up of the name of the scheme followed by a colon (“:”).
- authority: It is the hierarchical element that identifies the naming authority, it is form by the hostname and the port.
- path: It is the route that identifies the resource specific on the host which the consuming client wants to access, separating the hierarchical structure of resources with a slash (“/”)
- query: It is an optional component that is included after the path and has a non-hierarchical structure, and provides a string of information that the resource can use for some purpose, for example, to search parameters or data to be processed. The query is usually a string of pairs of parameters and values ("argument=value"). The arguments along with the values are separated from each other by an ampersand ("&")
- fragment: The fragment is an optional component that allows you to identify a part of the main resource, or view of a representation of it. The beginning of this component is indicated by the pound character (“#”)